In today’s IT landscape, enterprises are increasingly seeking multi-cloud environments as they offer them the flexibility to deploy workloads across diverse cloud platforms. Multi-cloud environment also reduces IT costs and complexity. Research conducted by TechTarget’s Enterprise Strategy Group (ESG) indicates that nearly 90% of IT decision makers consider it a strategic advantage to employ multiple cloud providers within their organizations.
In the research, IT leaders pointed out that the ability to customize infrastructure resources to meet the specific demands of various application environments was one of the chief benefits of a multi-cloud environment. By effectively optimizing workloads across multi-cloud environments, organizations can gain certain advantages.
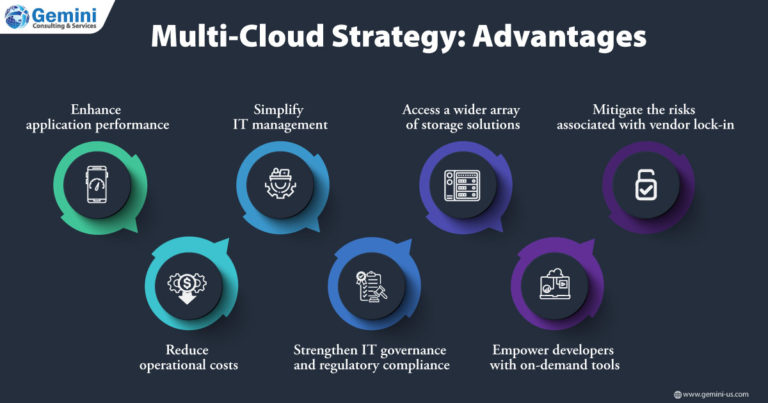
However, realizing the full potential of workload optimization within a multi-cloud framework presents its own set of challenges.
The Complexities of Multi-Cloud Workload Optimization
Multi-cloud adoption offers both advantages and disadvantages. The diversity and complexity of various cloud environments can lead to performance issues. The lack of interoperability and standardization among cloud services and APIs further compounds these challenges.
According to ESG’s findings, 82% of decision makers struggle with properly sizing workloads for optimal infrastructure placement, both on-premise and off. Moreover, 81% face difficulties in ensuring seamless application and data portability across different locations, including data centers, public clouds, and edge computing environments. Additionally, 83% express concerns over the costs and complexities associated with refactoring or re-platforming applications during cloud migrations.
Given the unique blend of workloads and business requirements within each organization, adopting a one-size-fits-all approach is impractical. Instead, the focus should be on enabling flexibility to leverage the most suitable deployment locations for different workloads. Even as organizations embrace a ‘cloud-first’ mentality, factors such as data governance, developer preferences, and total cost of ownership often affect decisions to deploy applications on-premise.
Building Successful Multi-Cloud Partnerships
Navigating the complexities of multi-cloud environments necessitates strong partnerships across the multi-cloud ecosystem. Collaborating with the right partners can help organizations minimize IT complexities and optimize workloads across diverse environments, thereby, unlocking the full potential of their multi-cloud strategy.
How to Select a Partner for Multi-Cloud Workload Optimization?
To leverage the full potential of multi-cloud IT, enterprises need to devise an optimal approach revolving around a multi-cloud strategy that’s integrated from the start. This involves a comprehensive suite of solutions that are neutral regarding workload placement, accessible across all primary infrastructure environments including public cloud, on-premises data centers, colocations, and edge computing.
Multi-cloud infrastructure and operations provide the agility to deploy workloads on any cloud platform necessary for business needs. Moreover, they facilitate the seamless migration, management, and security of applications irrespective of their deployment location. When executed effectively, a multi-cloud architecture empowers enterprises to accelerate their operations, reduce expenses, and mitigate risks across a distributed IT landscape.
At Gemini Consulting & Services, we specialize in assisting enterprises in preparing efficient multi-cloud strategies. Contact us to know how your organization can leverage the potential of multi-cloud IT through workload optimization.

Use Cases for Multi-Cloud Adoption
Industries such as logistics, retail, and manufacturing are witnessing the next wave of automation, efficiency improvements, and enhanced customer experiences, necessitating the distribution of applications to the edge. This entails deploying applications closer to physical devices and end-users.
Concerns regarding total cloud expenditure, data sovereignty, vendor dependencies, and lock-in are mounting. Consequently, enterprises are diversifying their infrastructure across various environments to maintain control and flexibility.
Distributed workforces have become commonplace in enterprises. Addressing the challenges of securing and managing users and their devices while enabling productivity from any location is the new hybrid workforce imperative. All these factors are leading to the increased adoption of multi-cloud environments.