We have witnessed an explosive growth in the digital ecosystem over the past decade. With a substantial increase in internet penetration and smartphone usage, the volume of personal data generated and processed has surged exponentially. This exponential growth in data usage underscores the need for a comprehensive data protection framework to safeguard the privacy and rights of individuals.
For the Internet to drive the benefits of improving every aspect of life that it permeates through today, we need to stand up to the challenge of protecting our data.
Individual choices in online activities, such as selecting robust passwords and exercising caution with email attachments, can significantly impact the overall security of networks. Heightened awareness of the far-reaching consequences of personal online actions is imperative.
Security companies face the challenge of developing solutions that are easy to use. Governments also play a crucial role in supporting infrastructure and internet policies that balance access and privacy. The mobile industry must devise sustainable business models ensuring privacy and access are intrinsic considerations from the inception of products.
Government authorities are tasked with making security and privacy universally comprehensible, simple, and pervasive. This approach will empower individuals to safeguard one of the most significant innovations of the last century—the internet—facilitating continued global development, innovation, and prosperity.
India, for example, enacted the Digital Personal Data Protection Act 2023, aiming to empower individuals and regulate the handling of personal data. The legislation mandates organizations to obtain informed and explicit consent before collecting and processing personal data, contributing to a more secure and privacy-conscious digital environment.

AI and Security Considerations
When artificial intelligence (AI) is employed for the analysis of personal data, entities in possession of such data gain unprecedented insights into individuals. This extensive knowledge, however, raises concerns about the potential misuse of the data. AI facilitates the collection of information from a larger yet more precisely defined pool, amplifying the risk of data misuse.
Conversely, AI can play a pivotal role in fortifying anonymization techniques designed to protect individual privacy. By eliminating personally identifiable information from datasets, AI minimizes the risk of re-identification. AI also contributes to the advancement of privacy-enhancing technologies, including encryption, secure protocols, and privacy-preserving algorithms.
With their ability to analyze and summarize privacy policies, AI can assist individuals in comprehending how their data will be utilized, shared, and safeguarded. Empowering individuals to make informed decisions about sharing their data contributes to increased transparency in data handling practices.
Enterprise and Data Security
The repercussions of data breaches extend to cost escalations. According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023, which assessed 553 organizations globally across various sizes, regions, and industries, the United States bears the highest average total cost of a data breach at $9.48 million, a slight increase from $9.44 million in 2022.
By 2025, the world is expected to safeguard a staggering 200 zettabytes of data. The escalating volume of data generated and consumed by organizations expands the attack surface for emerging cyber threats, necessitating urgent and effective data management and governance.
The regulatory landscape and compliance with regulations play a significant role in shaping the cost implications of data breaches. For an effective approach to data breach preparedness, Gemini Consulting & Services can help businesses integrate a proactive digital risk management strategy, emphasizing three core elements: people, processes, and technology. Contact us to learn more about the 10 practical strategies enterprises should adopt.
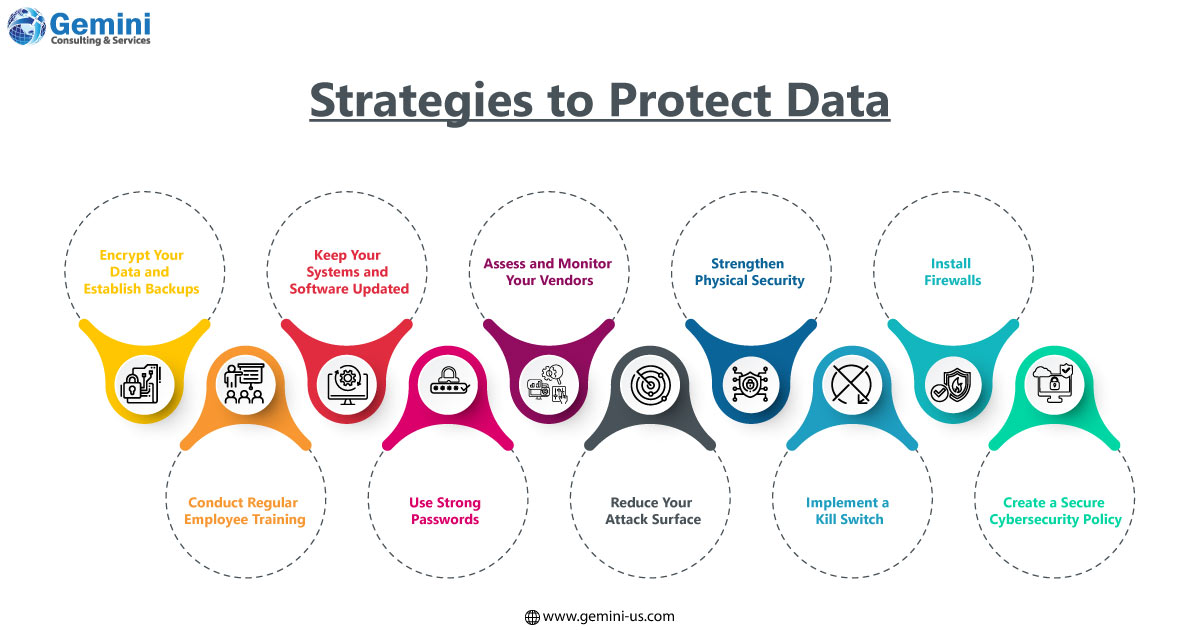
- Encrypt Your Data and Establish Backups
Ensure that sensitive data is encrypted, limiting access to authorized parties with encryption keys. Regular backups of crucial information should also be conducted to safeguard against potential data loss.
- Conduct Regular Employee Training
Mitigate the risk of malicious attacks via phishing emails by providing cybersecurity awareness training to employees. Educate them about various cybersecurity threats and best practices for prevention.
- Keep Your Systems and Software Updated
Regularly update software and systems to incorporate new features, fix bugs, and address security flaws. These updates are crucial for maintaining cybersecurity and digital safety.
- Use Strong Passwords
Adopt complex passwords and implement multi-factor authentication to deter cybercrime. Simple passwords are no longer sufficient considering the advancements in password-cracking technology.
- Assess and Monitor Your Vendors
Implement vendor risk management to mitigate third-party risks. Relying solely on incident response is insufficient, so proactive measures are essential.
- Reduce Your Attack Surface
Identify vulnerabilities or entry points that hackers could exploit. This is called surface analysis. Address security gaps to minimize potential attack vectors, including those associated with IoT, software, web applications, and susceptible employees.
- Strengthen Physical Security
Assess the security of physical premises to ensure protection against breaches. Analyze data protection policies and incorporate effective data disposal strategies.
- Implement a Kill Switch
Deploy a kill switch as a reactive cybersecurity protection strategy. This involves shutting down all systems upon detecting suspicious activity until the issues are resolved, providing protection against large-scale attacks.
- Install Firewalls
Defend networks from cyber-attacks by installing reliable firewalls. These systems safeguard against brute attacks, monitor network traffic for suspicious activity, and prevent unauthorized access, ensuring data integrity and privacy.
- Create a Secure Cybersecurity Policy
Craft a comprehensive cybersecurity policy that addresses data breach prevention and detection. Regularly assess the effectiveness of the policy, conduct risk assessments, and outline legal consequences for data mishandling to discourage insider attacks.