In 2025, manufacturers will continue their efforts to embrace digital transformation, though some may encounter difficulties in achieving meaningful returns from these initiatives.
Overall, investment in digital manufacturing is expected to rise in 2025. However, certain areas may see a slowdown in this trend. Forrester Research’s “2025 Predictions: Smart Manufacturing and Mobility” report outlines key trends and potential shifts in manufacturing investments.
The primary ongoing trend is the integration of digital technologies with physical assets and processes. However, some challenges persist, particularly as traditional manufacturers face difficulties in fully embedding digital technologies into their operations. Many companies are planning to transition from producing physical products to offering digitally enabled services, but this shift is proving more complex and resource-intensive than anticipated. As a result, some organizations may reconsider or scale back their ambitions after encountering these hurdles.
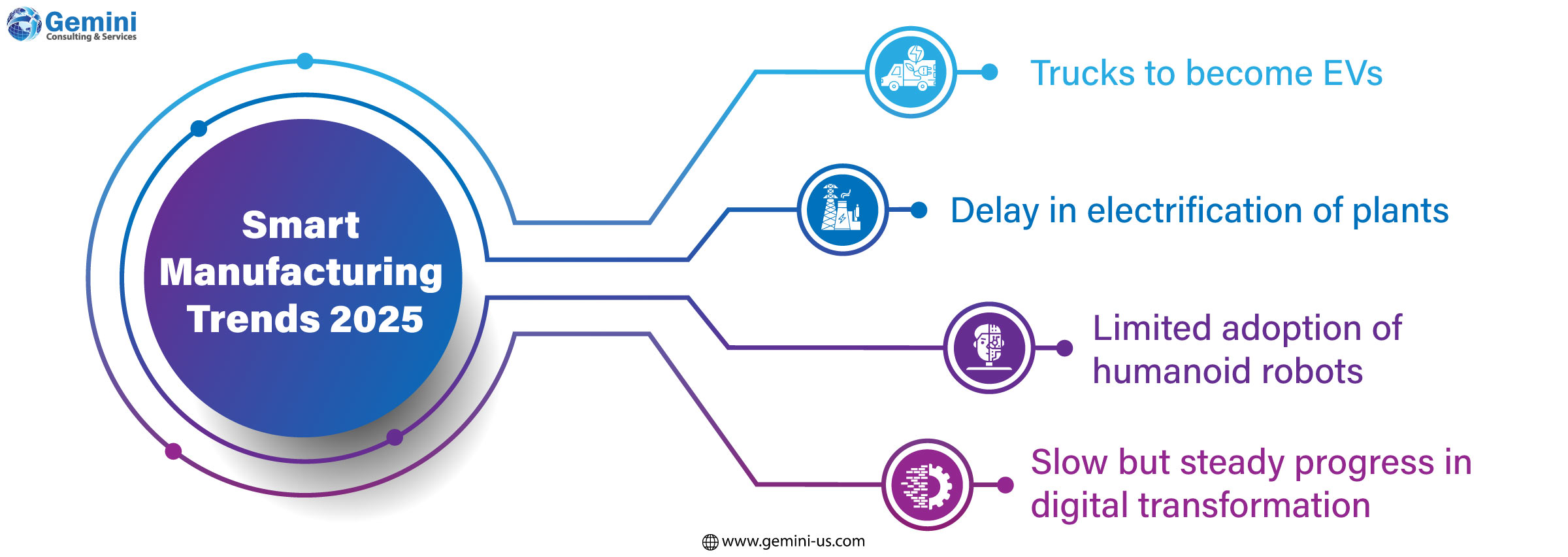
Forrester's report highlights four major trends influencing digital manufacturing in 2025.
- Electrification of Last-Mile Delivery Vehicles: The report predicts that 25% of large last-mile delivery vans in Europe will transition to electric vehicles (EVs), despite a slowdown in overall EV sales, particularly in the passenger vehicle sector. However, 50% of manufacturers may delay plans to electrify their operations. While electrification is seen as a way to reduce fuel costs and improve environmental sustainability, challenges such as insufficient grid capacity to accommodate increased demand are slowing the pace of adoption.
- Limited Adoption of Humanoid Robots: The hype surrounding humanoid robots in manufacturing is unlikely to translate into widespread deployment. Forrester forecasts that fewer than 5% of manufacturing robots will take on a human form, as the need for humanoid robots in manufacturing processes remains unclear. Most automation efforts are focused on task-specific robots that are optimized for stability and cost-effectiveness, rather than humanoid designs.
- Digital Transformation Challenges in Automotive Manufacturing: A major automotive manufacturer is expected to reduce its investment in digital development, following a lack of significant returns from digital services aimed at creating software-defined vehicles. Although many traditional carmakers are investing heavily in digitalization, they have yet to fully realize the expected benefits. Over the next year, they may shift their focus, seeking new partnerships and adjusting their strategies to deliver more measurable value in the digital space.
- Slow but Steady Progress on Digital Transformation: The digital transformation in manufacturing is progressing, though it remains an ongoing challenge. According to the 2024 State of Manufacturing Survey by Parsec Automation Corp., the digitization process is still in its early phases for many manufacturers. Half of the respondents reported either having completed (32%) or made significant progress (18%) in their digital transformation efforts, while 32% are still in the early stages, 15% are in the planning phase, and 3% are exploring options.
AI in Manufacturing: Growing Interest, But Slow Adoption
AI is one of the key technologies driving digital manufacturing, though widespread implementation remains limited. While there is growing interest, particularly in data analysis and predictive uses of AI, generative AI, which has gained prominence in other industries, is not suited for manufacturing’s needs. Generative AI excels in content creation, but manufacturing focuses more on predictive analytics and operational optimization.
Nearly half of survey respondents (47%) identified technical readiness as the biggest challenge to AI adoption, followed by issues with data accessibility and quality (44%). Despite these challenges, a majority of manufacturers (65%) report that they are either somewhat or very prepared to implement AI, with many actively working to educate their teams on how to leverage AI to improve operations.
If your manufacturing business is ready to embrace digital transformation and needs a trusted technology partner, Gemini Consulting & Services is here to assist. Contact us and consult with our experts to develop the ideal strategy for your organization.
Ultimately, for AI to reach its full potential in manufacturing, companies will need to train employees on how to use it effectively, with a focus on operational outcomes such as production schedules, quality metrics, and efficiency improvements.
In conclusion, while digital transformation is progressing across the manufacturing sector, it is clear that manufacturers face significant hurdles in fully realizing the benefits of these technologies. Over the coming years, these challenges will shape the strategies and investments in the industry as organizations work to refine their digital approaches and adapt to new technological realities.



