Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are critical to businesses, but whether hosted on-premises or in the cloud, they are susceptible to cyber threats. As supply chain attacks become more frequent, safeguarding ERP software has never been more important.
An ERP system is a goldmine of valuable data, from intellectual property to sensitive employee and customer information. This makes it a prime target for cybercriminals and malicious insiders. With the rise in supply chain attacks, it's essential for IT and security teams to fully understand ERP security risks to ensure long-term resilience.
Since ERP systems often house proprietary data, along with Personally Identifiable Information (PII) of employees and customers, it is vital to protect this information. Securing an ERP system can be challenging but is entirely achievable with disciplined, continuous efforts.
Why Are ERP Systems Vulnerable?
ERP security involves recognizing the weaknesses in and around the ERP environment and implementing the right safeguards to reduce risks. Regardless of whether the ERP system is cloud-based or on-premises, vulnerabilities are always present. Properly allocating resources to oversee all ERP components is crucial.
An ERP environment is inherently vulnerable due to its complexity. It consists of user accounts, network hosts, web components, databases, thick clients, and mobile applications—each of which can become a target. These complexities require constant vigilance from IT and security professionals.
As a seasoned provider of ERP solutions, Gemini Consulting & Services can help your enterprise safeguard your systems. Contact us to get a customized security plan implement it with the help of our ERP experts.
ERP systems, like any computer system, are susceptible to common security exploits, which can lead to serious issues if not addressed.
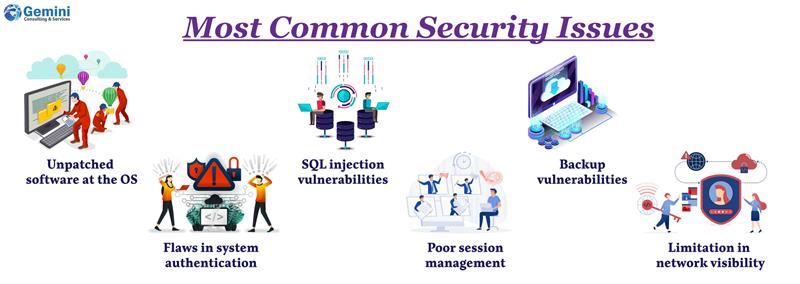
- Unpatched software at the operating system, application, and database levels, which can allow remote control, ransomware, or Denial of Service (DoS) attacks.
- Flaws in system authentication mechanisms that could expose user credentials or grant unauthorized access.
- SQL injection vulnerabilities due to inadequate input filtering.
- Poor session management or privilege escalation issues that create access control gaps.
- Backup vulnerabilities that leave systems open to ransomware attacks.
- Limitation in network visibility that impacts effective security incident response.
These security issues can impact enterprises of all sizes and industries.
Common Causes of ERP Security Incidents
In many organizations, ERP systems are primarily governed by internal or external audit teams, which focus on compliance and oversight. However, this audit-centric approach often neglects technical aspects such as vulnerability scanning and penetration testing. This gap in security oversight can lead to incidents that the core IT controls are supposed to prevent. Also, ERP systems are often not included in broader incident response and business continuity plans.
It is essential that executive leadership recognizes ERP security as a critical business priority, rather than simply an IT task to be delegated. Teams responsible for ERP management should collaborate across departments—IT, security, operations, finance, and legal—to establish clear metrics and make informed decisions about ERP security.
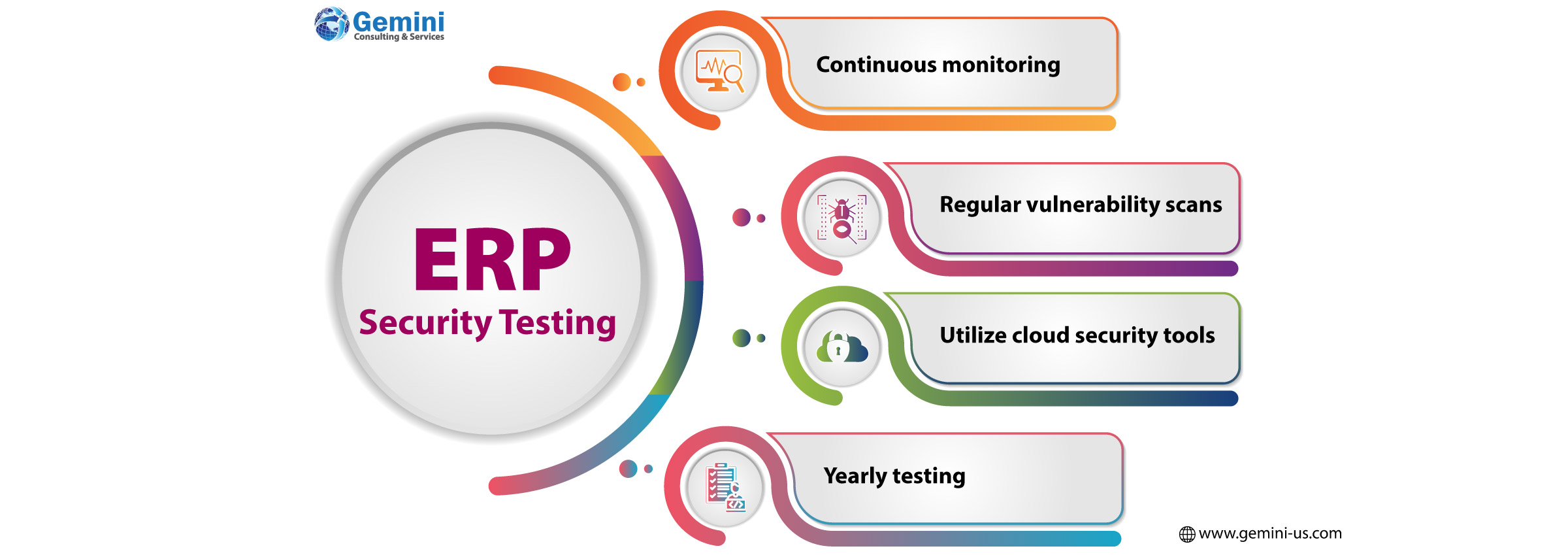
Regular testing is an essential component of ERP security. IT and security teams are responsible for continuously monitoring and evaluating ERP systems with various security technologies, such as logging, alerts, multifactor authentication, data loss prevention, and cloud access security brokers.
As part of ERP security best practices, IT teams should conduct regular vulnerability scans using network and web vulnerability scanners. These scans should be complemented by penetration testing and manual assessments since automated tools alone are insufficient. Additionally, database vulnerability scans and traditional network vulnerability scanners with database scanning capabilities can provide further insight into potential risks.
For cloud-based ERP systems, teams should also utilize cloud security posture management tools and firewall configuration analysis to ensure access is restricted to only those with a legitimate need.
ERP security testing should be conducted regularly—ideally at least once per year. If the organization relies on a third-party cloud-based ERP system, IT teams request recent vulnerability and penetration testing results.
Consistent oversight and a pragmatic approach are two often overlooked but crucial best practices in ERP security. The last thing any organization wants is to leave its most sensitive assets exposed due to preventable vulnerabilities. IT and security teams must ensure that their decisions are well-considered and defensible.



