With data coming to the centre stage in all process in an increasingly digitalized world, enterprises must devise strategies to protect their data. This article delves into how Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) can assist businesses in enhancing their data security by aligning with the core principles of the CIA triad: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability.
Understanding the CIA Triad: A Core Principle of Data Security

For many organizations, data is their most valuable asset, and maintaining its security is a regulatory requirement. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) defines three key pillars of information security:
- Confidentiality: Ensuring that sensitive data is only accessible to those with authorized access, and protecting both personal privacy and proprietary information.
- Integrity: Safeguarding data from unauthorized alterations or destruction, and ensuring the authenticity and non-repudiation of data.
- Availability: Ensuring timely and reliable access to data when needed.
Given the rising threat of cyberattacks such as ransomware, malicious insiders, and even accidental data breaches, it is crucial for organizations to detect and respond promptly to incidents that compromise data integrity. Businesses must be confident that such events are detected early and handled swiftly and effectively.
OCI Vault offers to protect data confidentiality and integrity. Others features such as storage replication within OCI Block Volumes ensure data availability. Together, these solutions help deliver comprehensive data protection.
Data Encryption in OCI
OCI offers robust data encryption features, with most data encrypted automatically using Oracle-managed keys. However, many businesses prefer the flexibility of using customer-managed keys (CMKs) for added control and security.
Data encryption in OCI relies on a Data Encryption Key (DEK) to secure your data, with a master encryption key responsible for encrypting the DEK. This multi-layered approach strengthens your data's protection against unauthorized access.
Let’s take a closer look at best practices for managing encryption keys within OCI.
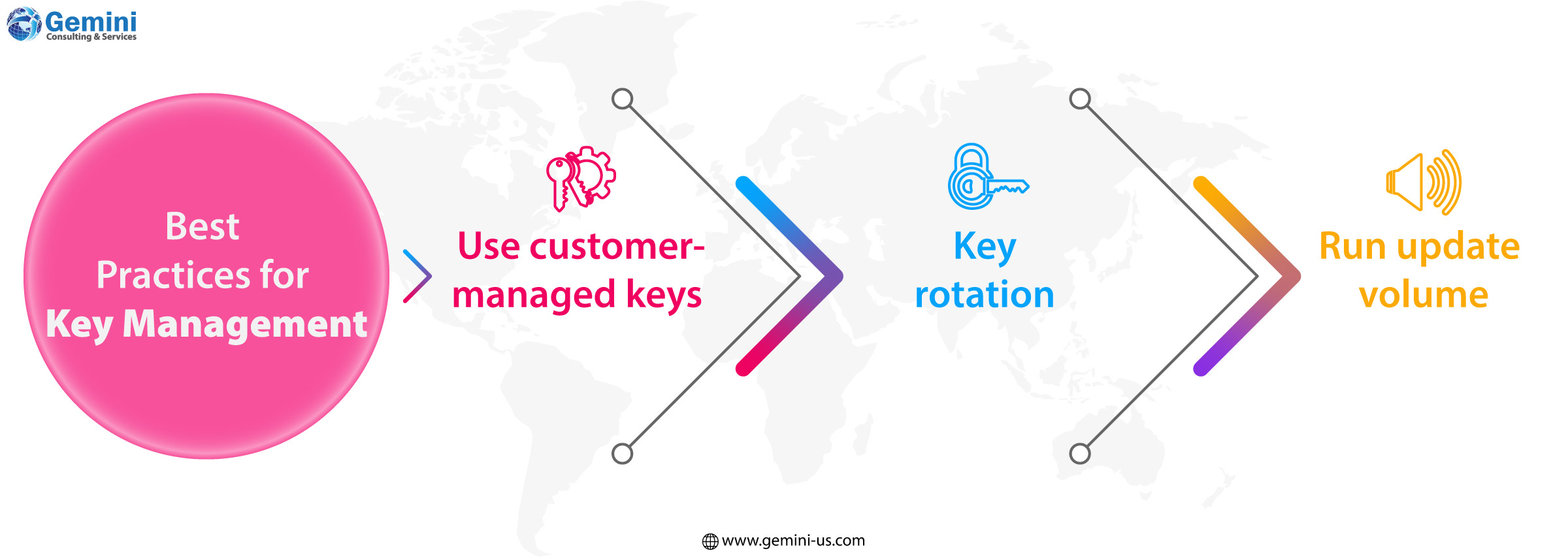
Oracle recommends using customer-managed keys to give organizations more control over their security. According to OCI best practices, it’s important to rotate keys periodically to minimize risks in case a key is compromised.
Key rotation involves updating the master encryption key (MEK), which in turn requires re-encrypting the associated DEK. It’s important to note that re-encrypting the DEK does not alter the data itself or affect the volume’s ability to access it. The rotation of the master encryption key only impacts customer-managed keys within a vault, and does not affect the availability domain (AD) master key. Key rotation activities in an AD are handled automatically.
Currently, Oracle does not support automatic updates for Block Storage volumes that use customer-managed keys through Key Management Service (KMS). When a KMS key is rotated to a new version in OCI Vault, the volume will continue to use the previous version until an update operation is manually performed. Running the “update volume” operation ensures that the latest key version is applied to your Block Volume, and this can be done without downtime.
It is crucial to follow best practices for key management, including the periodic rotation of keys, to ensure that your data remains secure even if a key is exposed.
If you’re looking to secure your data and optimize your cloud infrastructure, Gemini Consulting & Services can & support your journey to cloud security. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you safeguard your data on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
Conclusion
With OCI, businesses can achieve the highest levels of confidentiality, integrity, and availability for their critical data. Features like customer-managed keys for cross-region volume replication, as well as policy-based backup copies, further enhance your security posture.