Today’s developers face the challenge of developing and rolling out software at a faster pace without any compromise on quality. They need to look at tools that can mitigate the risks associated with the rapid development and deployment of applications. Submitting an IT ticket and waiting for months or even weeks for application updates is no longer an option in most companies.
Recognizing the requirement for efficient application development, SAP has introduced a suite of development tools. These tools are designed to facilitate seamless customization, strengthen integration capabilities, expedite development timelines, and ensure scalability.
In the initial segment of this two-part blog series, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of key SAP development tools integral to the software development lifecycle.
Exploring SAP Development Tools
SAP development tools serve diverse purposes across various stages of the software development lifecycle. They offer frameworks and environments catering to application development, integration, and application management. Encompassing functionalities such as programming, data modeling, and user interface (UI) design, these tools cater to a broad spectrum of professionals. Developers, data analysts, integration specialists, UI/UX designers, and system administrators working within SAP systems leverage these tools to enhance their respective areas of expertise.
Partner with Gemini Consulting & Services to leverage SAP development tools. Contact us to know how to stay efficient and competitive using these tools.
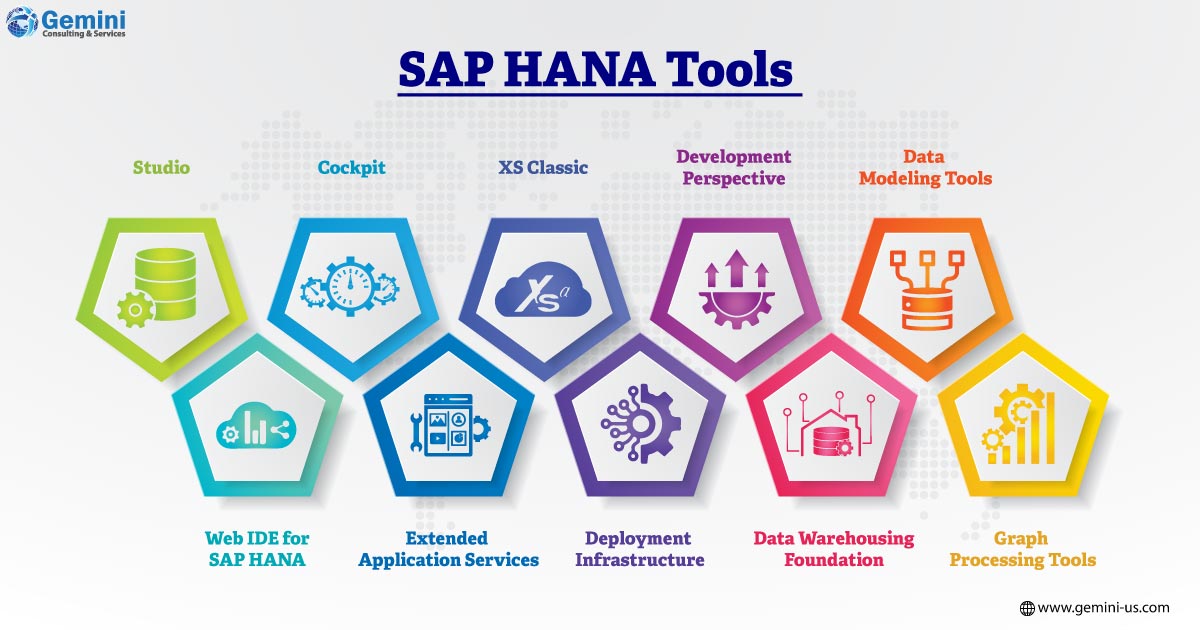
SAP HANA, an in-memory database excels in processing and analyzing vast amounts of data in real time. The diverse range of tools it offers supports multiple programming languages, data modeling techniques, and application development paradigms to cater to various development requirements.
SAP HANA Studio: An Integrated Development Environment (IDE) facilitating design, modeling, and data management. Comprehensive features encompass data modeling, SQL scripting, and administration.
SAP Web IDE for SAP HANA: Web-based development tool with a user-friendly interface. Specialized in UI design, server-side JavaScript coding, and seamless integration with SAP HANA databases.
SAP HANA Cockpit: Web-based administration and monitoring tool. Centralized dashboard for monitoring system health, performance, and resource utilization. Capabilities extend to user, role, and security management.
SAP HANA Extended Application Services (XSA): Application server for building and deploying applications directly on SAP HANA. Supports both database-side and application-side development using JavaScript, Node.js, and SQLScript.
SAP HANA XS Classic: Runtime environment for developing and deploying applications. Facilitates server-side JavaScript programming and enables direct interaction with the database.
SAP HANA Deployment Infrastructure: Runtime and development environment for creating and managing database artifacts. Allows packaging of database objects, application logic, and configuration files as deployable units.
SAP HANA Development Perspective in SAP Business Application Studio: Development environment for SAP HANA with tools for tasks such as designing tables, creating calculation views, and writing SQLScript.
SAP HANA Data Warehousing Foundation: Set of tools and frameworks enabling the development of data warehousing solutions on SAP HANA. Features data provisioning, data modeling, and data lifecycle management.
SAP HANA Data Modeling Tools: Tools for creating and managing data models, including attribute, calculation, and analytical views. Encompasses the SAP HANA Modeling perspective in SAP HANA Studio and SAP Web IDE for SAP HANA.
SAP HANA Graph Processing Tools: Tools for creating applications leveraging graph-data processing capabilities in SAP HANA. Offers features for creating and querying graph data models.
SAP Cloud Business Application Tools
SAP’s suite of cloud-based business application tools facilitates the development and deployment of applications in a cloud environment. These resources empower developers to create applications compatible with the SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP), a comprehensive set of tools and services for extending and building SAP applications. Functionality includes workflow automation, document generation, and integration with external systems.
One such tool is the web-based integrated development environment (IDE), SAP Business Application Studio, designed for cloud-native application development. This platform, an open enterprise solution, incorporates built-in governance, security, and DevOps features. Users can seamlessly integrate with various services, technologies, and systems offered by SAP, enabling the design, coding, and deployment of applications in multiple programming languages.
The SAP Cloud Application Programming Model provides guidelines and tools for developing enterprise-grade applications across multiple cloud platforms running on SAP BTP. Additionally, SAP Fiori tools support the design and deployment of user-friendly interfaces. For mobile application development and management, SAP Mobile Services offers specific features. This suite of tools allows both developers and business users to create customized solutions tailored to specific business requirements.
Additional SAP cloud-based business application tools include the SAP Cloud Application Programming Model Tools for Visual Studio Code, an extension providing extra tools for modeling and application development. The SAP Extension Suite is a comprehensive package of tools and services for building and extending SAP applications, offering capabilities such as workflow automation, document generation, and external system integration. Lastly, the SAP BTP, ABAP Environment, provides a platform for developing ABAP-based cloud applications within the SAP BTP ecosystem.

ABAP Development Tools
ABAP Development Tools (ADT) serve as SAP’s exclusive programming language, offering developers a suite of tools to create, modify, and manage ABAP code. The ADT, constituting a comprehensive Integrated Development Environment (IDE), incorporates essential features like syntax highlighting, code completion, and a robust debugger to facilitate efficient code development and debugging processes. Additionally, it includes a repository browser for easy navigation through SAP’s repository objects and a transport organizer for managing software requests across different systems. The code inspector within ADT functions as a tool for conducting static code analysis, ensuring the quality and efficiency of ABAP code.
Various ADT components, such as SAP S/4HANA Cloud, ABAP environment, and SAP BTP, ABAP environment, can be installed. Developers leverage these components to customize standard SAP functionalities, create custom reports and interfaces, implement business logic and workflows, and integrate external systems with SAP.
SAP Business Warehouse (BW) Modeling Tools
SAP BW/4HANA serves as a warehousing solution running on the SAP HANA database, aimed at consolidating, transforming, and analyzing data from diverse sources. The modeling tools in SAP BW/4HANA are instrumental in designing data models, defining data sources, and creating data transformations.
These tools support the creation of InfoProviders and InfoObjects, enabling businesses to structure and manage their data efficiently. SAP BW/4HANA provides capabilities for data staging, storage optimization, data compression, and aggregation – all critical aspects for optimizing performance in reporting and analysis. Data analysts and developers depend on these tools to establish a structured and effective warehouse environment.
Integrating SAP BW/4HANA with ABAP Development Tools and SAP HANA modeling results in the creation of SAP HANA views usable in BW metadata objects, such as the CompositeProvider. This integration facilitates the flexible and efficient execution of modeling projects