SAP applications are designed to help businesses improve efficiency and deliver a better experience to customers. These business applications also provide users with complete access to information, helping them make faster decisions based on data and gain a competitive advantage in any industry. A full-proof testing phase is an important requirement for building and deploying new bug-free versions of SAP applications.

What Entails SAP ERP Testing?
SAP ERP applications comprise several specific interdependent modules, the architecture of which is quite sophisticated and complex. Hence integration testing and performance testing are key to evaluating the success of the SAP ERP application; particularly when businesses rely on SAP to run vital business processes. Testing customizations, updates, and integrations with other applications impact the continued functionality of SAP. Let us understand all of these processes in detail.
- In SAP, customizations are termed as WRICEFs which is an SAP acronym that stands for Workflow, Report, Interface, Conversion, Enhancement, and Forms. Since default features may not be sufficient to meet the business requirements of all enterprises, customizations are carried out and these need to be tested periodically to ensure that the chances of errors are minimal.
- Whether the business is powered by SAP S/4HANA (where updates are more regular) or by any other SAP module, updates cause some disruptions in the ongoing business process. Testing helps to ensure that disruptions are handled properly, and bugs are found and corrected before anything is released to a live environment.
- A business process can run across more than one module and extend beyond SAP to other applications say MS Excel/Outlook or a legacy system like Mainframe, and/or a web application like Salesforce. Integrations also need to be tested as much as customizations and configurations.
- In case the business is transitioning to SAP S/4HANA (which is more common now), they have to work with a deadline for 2027. By this time, SAP ECC will transition to S/4HANA for easier use and the capability to handle more data. Therefore, the need to test their solution, processes, and integrations has become a pre-requisite. These tests may also include doing end-to-end automation in and outside of SAP, generating master data, and building flows to verify processes for the move.
Gemini Consulting & Services has a group of reliable and experienced testing experts who can conduct different types of SAP testing to handle changes in ERP applications. This helps fix issues and patch management, making it easy to implement new modules, or update configurations. It also improves efficiency and keeps the database of information reliable. Contact us to understand how testing can lead to faster software release cycles and enhance the efficiency of your SAP environment.
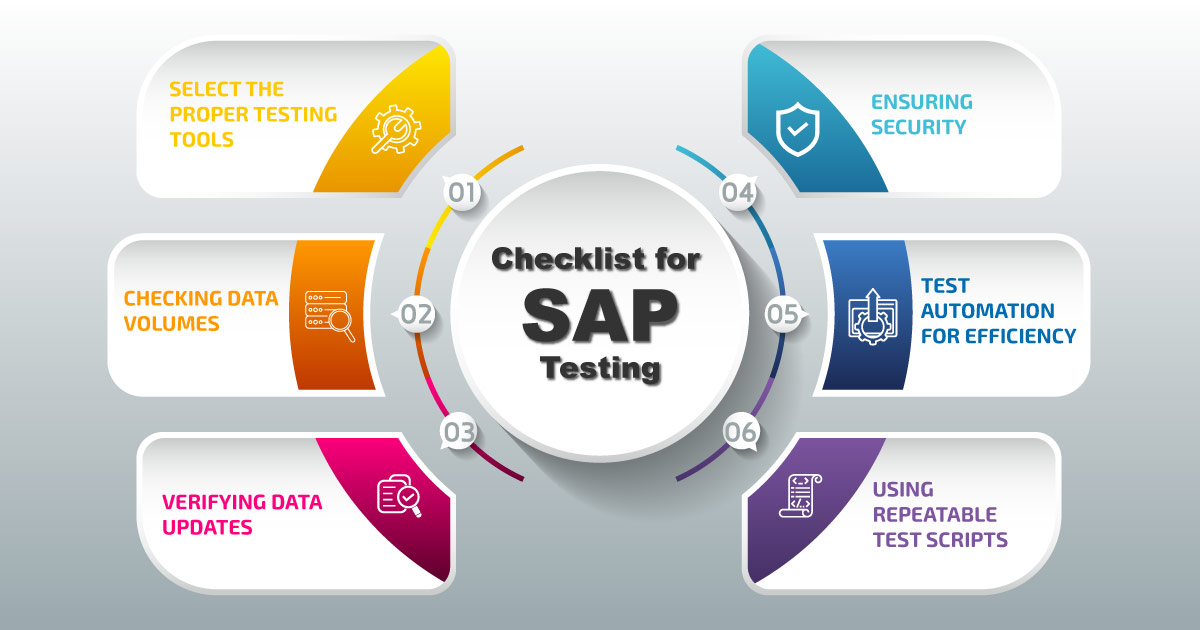
Best Practices for SAP ERP Testing
- Type of SAP application in use
Based on the SAP ERP application used, the required SAP testing tools applicable and to be selected varies. Since SAP ECC depends on certain legacy technologies like SAP GUI, testing changes carried out there need SAP-focussed tools, languages (SAP ABAP), and framework libraries.
- Matching the data volumes as per need
When the data is provisioned for testing in SAP, different types of testing can be done. If the data is established in a unit testing client in the development, data volumes can be small and isolated to the specific process to be tested. Therefore, there is no need to replace large volumes of data in a development system, not intended or suitable for performance testing. As the business looks higher up the transport path, individual data sets will suffice for production support issues. Sometimes during the integration testing, most organizations will require some performance testing before going to production. This gives rise to a need to consider client sub-setting or in some cases demand a partial or full history of transactions.
- Handling production data
Businesses particularly those in FMCG and retail may have a requirement to update some testing data, without damaging other data. Some parts of a material master could have been updated in the test system, say, extending material to a new plant. This cannot be overwritten but carrying on testing without the latest pricing conditions or new vendors/customers which have been recently created in production may be needed. Such circumstances demand absolute precision in the identification of data and filtering options chosen.
- Security policies and masking sensitive data
Without the ability to mask labels and identifiers, companies will revert to asking the testers to create the data. Now the risk here is that the resources involved in the role may influence the process and the data should be considered as per their opinions. Unusual data cases are often the ones that spring in testing and highlight tough bugs.
- Automated testing processes
It is nearly impossible to have the entire digital transformation journey via SAP tested manually and therefore the concept of SAP test automation makes an entry. Test automation for SAP deals with leveraging automation tools and platforms and combining best practices to enable a seamless and automated testing experience for digital systems. SAP test automation helps development and testing teams to accurately verify and validate customizations and new feature development initiatives. This fosters business agility as automated testing has grown to become quicker and easier to schedule. You can read more about testing tools in our blog here.
- Using simple, focused test scripts
If the data and exact testing process are identified and recorded, simple consistent, and repeated testing approaches can be enabled. With a catalog of repeatable test scripts, the reliability of development codes goes up, and automation becomes much simpler. This way manual testing can be reserved only for new or complex/critical cases.
Any inconsistency in service quality or errors in live systems can throw the business’s core functions and disrupt business workflows off track for a while. This results in the lack of availability of key systems, thereby, affecting customer experience. SAP testing validates the functionality of SAP modules to ensure that they conform to perform as intended.